For individuals with respiratory conditions, maintaining adequate oxygen levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Home oxygen therapy has become an essential component of treatment for many patients, allowing them to breathe easier and improve their quality of life. This article explores the various home oxygen supply options available, including machines, tanks, and essential medical accessories, to help you make informed decisions about your oxygen therapy needs.
Understanding Home Oxygen Therapy
Home oxygen therapy involves the use of supplemental oxygen to assist individuals who have difficulty breathing due to chronic respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or pulmonary fibrosis. The primary goal of this therapy is to increase the amount of oxygen in the blood, thereby alleviating symptoms and enhancing the patient’s ability to engage in daily activities.
Home oxygen supply therapy is a vital component of managing respiratory conditions, and understanding the various supply options available can empower patients and caregivers to make informed decisions. From oxygen concentrators to compressed tanks and essential accessories, each option has its unique benefits and considerations. By evaluating lifestyle, flow rate requirements, and financial factors, individuals can select the most suitable home oxygen supply to enhance their quality of life and ensure effective treatment.

Before starting home oxygen therapy, a healthcare professional will assess the patient’s oxygen levels through various tests, including arterial blood gas analysis or pulse oximetry. Based on the results, a tailored oxygen therapy plan will be developed, which may include the type of oxygen delivery system, flow rate, and duration of use.
Types of Home Oxygen Supply Options
There are several types of home oxygen supply options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options can help patients and caregivers choose the most suitable solution for their needs.
Find more at: Best Portable Oxygen Concentrators in Australia Top Picks for 2025
1. Oxygen Concentrators
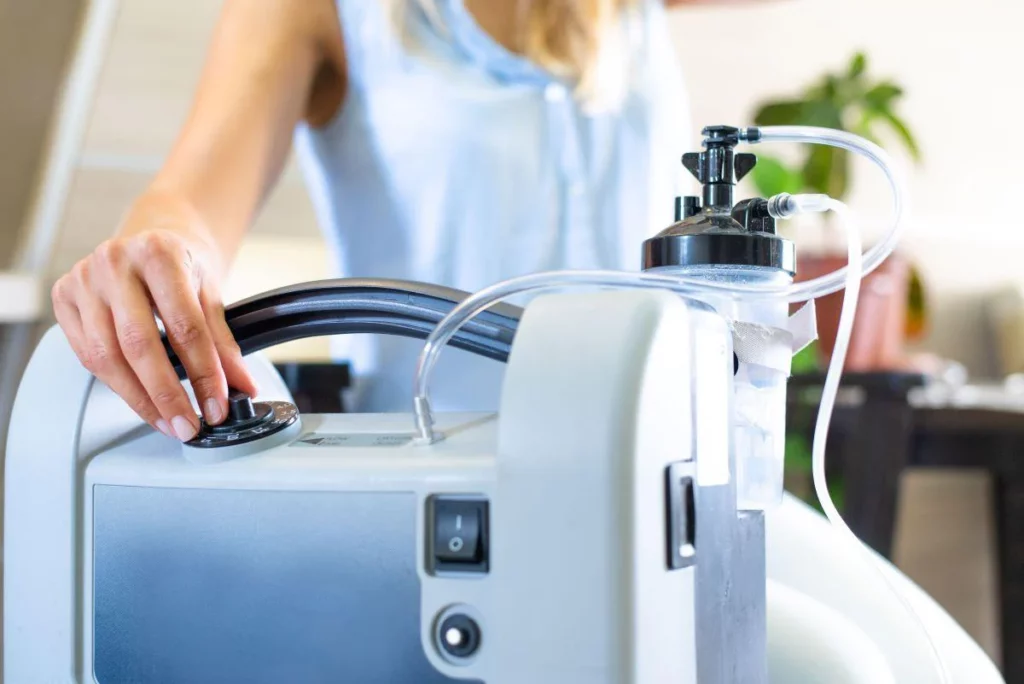
Oxygen concentrators are electrically powered devices that extract oxygen from the surrounding air and deliver it to the patient. They are popular for home use due to their convenience and continuous supply of oxygen, eliminating the need for refills.
These machines are available in two main types: stationary and portable. Stationary concentrators are designed for home use and typically provide higher flow rates, while portable concentrators are lightweight and battery-operated, allowing for mobility outside the home.
- Advantages: Continuous supply, no need for refills, and can be used for long periods.
- Disadvantages: Requires electricity, which may limit use during power outages.
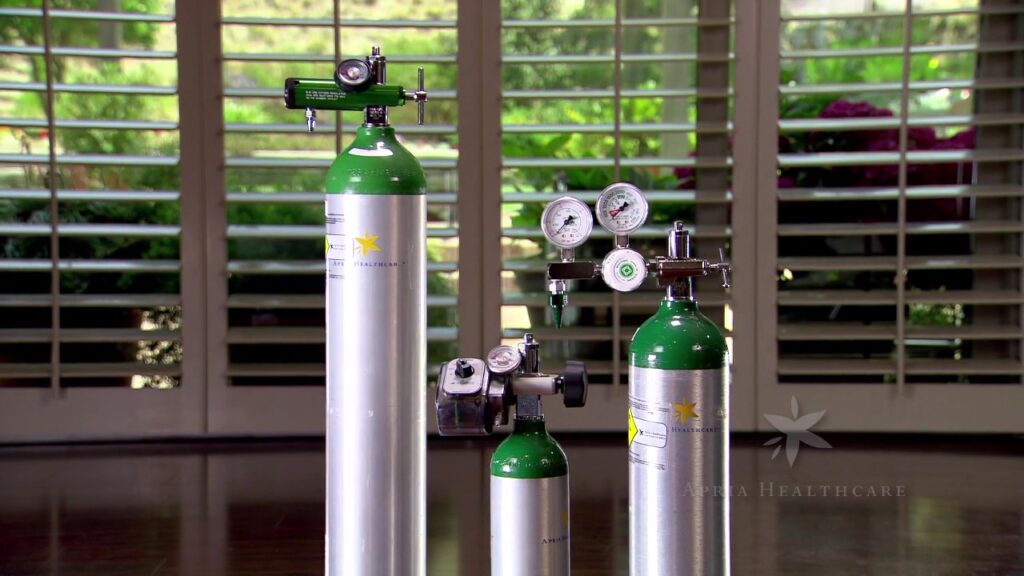
2. Compressed Oxygen Tanks
Compressed oxygen tanks are high-pressure cylinders that store oxygen in liquid form. They are available in various sizes, making them suitable for different needs, from small portable tanks to larger stationary units.
These tanks are often used in conjunction with a regulator that controls the flow of oxygen to the patient. They are ideal for individuals who require oxygen therapy while travelling or during outdoor activities.
- Advantages: Portable, can be used without electricity, and available in various sizes.
- Disadvantages: Limited supply, requiring regular refills, and can be heavy and cumbersome.
3. Liquid Oxygen Systems
Liquid oxygen systems store oxygen in a cryogenic liquid state, allowing for a larger volume of oxygen to be stored in a smaller container. These systems are often used for patients who require higher oxygen flow rates or need to be mobile. Raed more about liquid on https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10052594/
Liquid oxygen is dispensed into portable containers that can be carried around, providing patients with the flexibility to move freely while receiving their oxygen therapy.
- Advantages: High oxygen capacity, lightweight portable containers, and can be refilled from a larger stationary unit.
- Disadvantages: Requires careful handling due to the extremely low temperatures, and may not be as widely available as other options.
Medical Accessories for Home Oxygen Therapy
In addition to the primary oxygen supply options, various medical accessories are essential for ensuring effective and safe oxygen therapy. These accessories enhance the user experience and help maintain the equipment.
1. Oxygen Delivery Devices
Oxygen delivery devices are crucial for administering oxygen to the patient. The most common types include nasal cannulas, face masks, and transtracheal catheters. Each device has its own advantages and is chosen based on the patient’s specific needs.
- Nasal Cannulas: Lightweight and comfortable, ideal for low-flow oxygen therapy.
- Face Masks: Provide a higher concentration of oxygen and are suitable for patients requiring higher flow rates.
- Transtracheal Catheters: Inserted directly into the trachea, these are used for long-term oxygen therapy and provide a more discreet option. Click here to find more about comfortable.
2. Humidifiers
Oxygen therapy can sometimes lead to dryness in the airways, making humidifiers an essential accessory. These devices add moisture to the oxygen being delivered, helping to prevent irritation and discomfort.
Humidifiers can be integrated into oxygen concentrators or used as standalone units. They are particularly beneficial for patients who require long-term oxygen therapy or those who experience dryness or irritation in their nasal passages.
3. Oxygen Regulators and Flow Meters
Oxygen regulators and flow meters are essential for controlling the amount of oxygen delivered to the patient. Regulators reduce the high pressure from the oxygen tank to a safe level, while flow meters allow for precise adjustments to the flow rate.
These devices ensure that patients receive the appropriate amount of oxygen as prescribed by their healthcare provider, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the therapy.
Considerations When Choosing Home Oxygen Supplies
When selecting home oxygen supply options, several factors should be considered to ensure that the chosen system meets the patient’s needs effectively.
1. Lifestyle and Mobility
The patient’s lifestyle plays a significant role in determining the most suitable oxygen supply option. For individuals who are active and frequently travel, portable oxygen concentrators or compressed oxygen tanks may be more appropriate. Conversely, those who spend most of their time at home may benefit from a stationary oxygen concentrator.
2. Flow Rate Requirements
The prescribed flow rate of oxygen is another critical factor to consider. Patients with higher oxygen needs may require larger tanks or more powerful concentrators, while those with lower needs may find smaller, more portable options sufficient.
3. Cost and Insurance Coverage
Cost is an important consideration when selecting home oxygen supplies. Patients should explore their insurance coverage options, as many providers cover a portion of the costs associated with oxygen therapy. It’s advisable to consult with healthcare professionals and suppliers to understand the financial implications of different oxygen supply options.

